Assam General Knowledge MCQs | Most Important Questions For APSC: The word Assam is derived from Sanskrit word Assama meaning peerless or unparalled. But widely accepted opinion, the word has come from the original name of the Ahoms, who ruled the land of Assam for about 600 years. History of ancient Assam comes from rock inscriptions and the many copper plates and royal grants the Kamrup kings issued. In the Epics, Assam was known as Kamrupa or Pragjyotispura.
Although additional changes to India’s state boundaries have been made since 1956, the States Reorganisation Act of 1956 remains the most extensive change in state boundaries after the independence of India.
The Act came into effect at the same time as the Constitution (Seventh Amendment) Act, 1956, which (among other things) restructured the constitutional framework for India’s existing states and the requirements to pass the States Reorganisation Act, 1956 under the provisions of Part I of the Constitution of India, Article 3.
The new Constitution of India, which came into force on 26 January 1950, made India a sovereign democratic republic. The new republic was also declared to be a “Union of States”. The constitution of 1950 distinguished between three main types of states and a class of territories:
Part A states – which were the former governors’ provinces of British India, were ruled by a governor appointed by the president and an elected state legislature. The nine Part A states were Assam, Bihar, Bombay, Madhya Pradesh (formerly Central Provinces and Berar), Madras, Odisha (formerly Orissa), Punjab (formerly East Punjab), Uttar Pradesh (formerly the United Provinces), and West Bengal.
Part B states – which were former princely states or unions of princely states, governed by a Rajpramukh, who was usually the ruler of a constituent state, and an elected legislature. The raj Pramukh was appointed by the President of India. The eight Part B states were Hyderabad, Jammu and Kashmir, Madhya Bharat, Mysore, Patiala and East Punjab States Union (PEPSU), Rajasthan, Saurashtra, and Travancore-Cochin.
Part C states – included both the former chief commissioners’ provinces and some princely states, and each was governed by a chief commissioner appointed by the President of India. The ten Part C states were Ajmer, Bhopal, Bilaspur, Coorg, Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Cutch, Manipur, Tripura, and Vindhya Pradesh.
Also, check: General Studies of Assam PDF | Assam General Knowledge
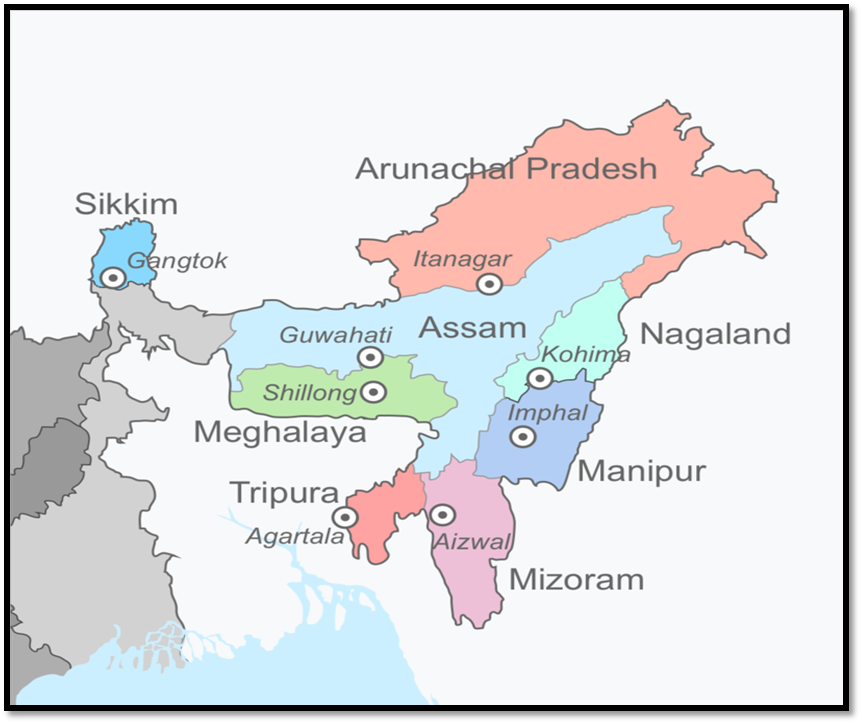
Assam shares Interstate boundary with West Bengal, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Tripura, Nagaland, Manipur and Mizoram.
The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur to the east; Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram and Bangladesh to the south; and West Bengal to the west via the Siliguri Corridor, a 22-kilometre-wide (14 mi) strip of land that connects the state to the rest of India. Assam shares Interstate boundary with West Bengal, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Tripura, Nagaland, Manipur and Mizoram.
Assam General Knowledge MCQs For APSC
1. In 640 A D. Chinese traveller Hiuen Tsang visited Assam (Kamrupa). The king who gave him warm reception was
(a) Kumar Rudra Barmana
(b) Swargadeo Rudra Singha
(c) Kumar Bhaskara Barmana
(d) Bhagadatta
2. Which one of the following was the last capital of Ahom dynasty?
(a) Nazira
(b) Sivasagar
(c) Charaideo
(d) Jorhat
3. In which year the first newspaper of Assam ‘Orunodoi’ was published?
(a) 1899
(b) 1824
(c) 1830
(d) 1846
4. The ancient name of Assam as mentioned in epics Ramayana and Mahabharata is
(a) Indraprastha
(b) Kamrup
(c) Ahom
(d) Pragjyotishpura
5. The state of Assam has …… representatives in the Rajya Sabha.
(a) 5
(b) 12
(c) 7
(d) 13
6. The rare white-winged duck (Deohanh) is found in which of the following National Park of Assam?
(a) Kaziranga National Park
(b) Manas
(c) Dibru Saikhowa
(d) Nameri
7. A famous musical instrument of Assam ‘GAGONA’ is made of which material?
(a) Cane
(b) Buffalo horn
(c) bamboo
(d) teak wood
8. Which one of the following was the earliest historical dynasty of Assam?
(a) Varmans
(b) Narakas
(c) Salastambhas
(d) Palas
9. The state of Assam has …… representatives in the Lok Sabha?
(a) 12
(b) 15
(c) 14 (d) 18
10. Who was the first Assamese person to receive the title of ‘Sir’ from the British?
(a) Sir Syed Ahmad
(b) Sir Akbar Hydari
(c) Sir Saiyyid Sadullah
(d) None of the above
11. In which year Panchayati Raj was formally introduced in Assam?
(a) 1962
(b) 1964
(c) 1969
(d) 1970
12. Which one of the following was the royal symbol of the kings of ancient Kamrupa?
(a) elephant
(b) lion
(c) tiger
(d) rhinoceros
13. Which one of the following district of Assam shares the longest international boundary?
(a) Karimganj
(b) Kokrajhar
(c) Silchar
(d) Dhubri
14. In which year Assam Pradesh Congress Committee was founded?
(a) 1909
(b) 1912
(c) 1917
(d) 1921
15. Who among the following Assamese leader was a member in the Constitution Drafting Committee?
(a) Mohammad Sadullah
(b) Rohini Kumar Chaudhary
(c) Gopinath Bardoloi
(d) None of the above
16. In which of the following cities ‘Gibon Wildlife Sanctuary’ is located?
(a) Kokrajhar
(b) Jorhat
(c) Dibrugarh
(d) Chirang
17. The first President of the ‘Assam Pradesh Congress Committee’ was
(a) Gopinath Bordoloi
(b) Nabin Chandra Bordoloi
(c) Kuladhar Chaliha
(d) Tarun Ram Phukan
18. The Guwahati Stock Exchange was established in Assam in which of the following years?
(a) 1984
(b) 1989
(c) 1987
(d) 1983
19. Who among the following was the first Assamese to be appointed as a judge in the Supreme Court of India?
(a) Mahendra Mohan Chaudhary
(b) Parbati Kumar Goswami
(c) Ranjan Kumar Gogoi
(d) None of the above
20. Which one of the following cities is also known as the ‘Manchester of Assam’?
(a) Diphu
(b) Jorhat
(c) Saulkuchi
(d) Digboi
Also, check: Assam Current Affairs Yearly 2025-26 PDF
Answers:
1. (c) 2. (b) 3. (d) 4. (d) 5. (c) 6. (d) 7. (c) 8. (b) 9. (c) 10. (c) 11. (b) 12. (a) 13. (d) 14. (d) 15. (a) 16. (b) 17. (c) 18. (d) 19. (c) 20. (c)